Introduction
Healthcare has always been one of the most strictly regulated industries across the globe, and in 2022, compliance and security for digital healthcare solutions keep surging in demand. Ever since the beginning of the Information Age, the healthcare industry has operated with massive amounts of personal and clinical data, posing major challenges for healthcare providers, medical companies, and individual practises. Adequate digital healthcare solutions are required to handle all this available medical data, make sense of it and achieve better care quality. Plus, the constantly rising market demands provoke the sector to seek innovative ways to engage with patients, thus the emerging trends of personalisation, patient-centricity and data security.
Working in a product development company in digital healthcare makes me see all the unexplored potential of new software technologies in this medical context. The constant need to optimise and achieve more sustainable workflows has far bigger implications for healthcare entities than just financial progress. The recent shift towards value-based healthcare models urges providers to readapt their care delivery, derive actionable insights from data-driven analytics and prioritise personal data security. Before we explore the available solutions, let us explore the main areas around compliance and security in digital healthcare.
Compliance and Security in Healthcare: Key Elements
When we say compliance and security, what do we exactly mean by that? What are the key components that we need to take into account?
Experts put cybersecurity as a number leading area of concern regarding compliance and security, particularly in healthcare. The US National Center for Biotechnology Information defines the target subjects of concern as sensors, apps, research databases, websites, electronic health records (EHR), patients, and the general population. And the ways through which they may be affected are data leakage, phishing and other types of attacks on mobile devices, emails, Internet communication security, and the cloud.
In its cybersecurity section, the FDA shared a threat modelling playbook that defines key elements of contemporary threat risks and models to identify them.
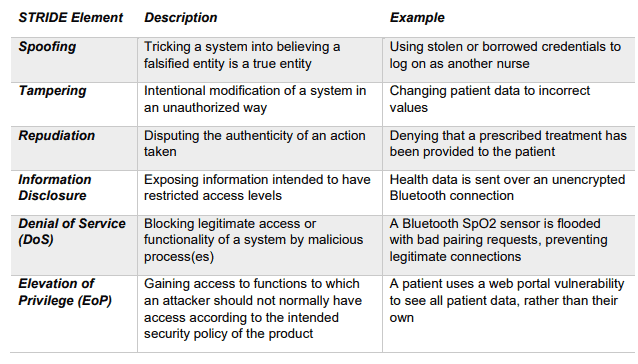
Source: Playbook for Threat Modelling Medical Devices.
In the document, there are also three available and free threat modelling solutions: Microsoft Threat Modelling, IriusRisk, and the OWASP Threat Dragon.
Compliance and security solutions, however, need to be implemented holistically and with individual entities’ needs and specifications taken into account. Based on the markets on which you operate, you need to comply with local specific regulations in both data protection and healthcare records. You also need to comply with your vendors’ requirements and their own standards in the field. So let us first see what the local regulations say about digital healthcare compliance and security.
EU, UK, and US Main Regulations for Digital Healthcare Compliance and Security
Below are some of the must-know laws and regulations regarding digital healthcare solutions in 2022 combined with expert IT advice for effective adoptions.
EU Policy for Healthcare
Like most of the EU’s political frameworks, the digital healthcare one is divided into pillars. A Europe fit for the digital age is one of the main political priorities of the EU Commission for the period 2019-2024. The transformation to digital technology should benefit the people first and they should be at the centre of it. Therefore, the Commission issued its 2018 communication into three main pillars:
- Pillar 1: Secure data access and sharing
To facilitate cross-border digital healthcare, the Commission is designing the eHealth Digital Service Infrastructure, including the service named MyHealth: a digital service infrastructure. It includes ePrescription and eDispensation and Patient Summaries, including medical images, lab results, hospital discharge reports, etc. All of this will be adopted in 25 EU member states by 2025.
- Pillar 2: Connecting and sharing health data for research purposes, a quicker diagnostic process and improved health
This pillar aims to facilitate the use of huge amounts of data in order to help scientific discoveries, prevention, treatments, etc.
- Pillar 3: Empowering public and individual care through digital services
Pillar 3 focuses on personal health management through the means of chronic conditions management and consistent healthcare providers’ feedback
EU Regulation
The EU-wide first guideline that comes into mind when it comes to data protection is the 2018 General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The GDPR outlines rules for collecting, processing, and securing personal data. Healthcare organizations are key as they hold patients’ and medical research’s huge quantities of data that are even more sensitive than the average industry’s.
Article 4(15) GDPR formulates health data as personal data that has to do with the physical or mental health of individuals and the provision of health-related services that contain sensitive information regarding their health status.
To process special category data, you should associate both Article 6 GDPR and Article 9 GDPR.
UK Core Legal Issues
With UK government regulations and healthcare technology becoming more complex and patient expectations rising, healthcare providers need to consistently adapt their new and existing technology to the updated laws.
Despite Brexit, the UK will continue to comply with GDPR as its main data protection legislation. In addition, healthcare entities in the UK or working with the UK must also comply with the Data Protection Act from 2018.
In terms of consumer devices, in particular, a new mark will take effect starting from July 1, 2023: the UK Conformity Assessed. Compliance with the UKCA marking should be maintained by a nominated responsible person.
US Main Legislation
The main data privacy instrument in the US healthcare legislation is HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) from 1996. However, there are a few more that are key to your healthcare entity: the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH Act).
If we regard digital healthcare through the prism of its specific technical means, there are a few additional regulations that the International Comparative Legal Guide defines, such as:
- For telemedicine – data rights to health data, SaMD, 510k and PMA
- For mobile apps – tort liability for injury.

Types of Solutions
So now you already know that when you manage a digital healthcare product, you need to take into account all the threats and regulations. And here comes the bittersweet part: what you should do about it! The Digital guardian defines 10 key steps to secure your project.
- Educate healthcare staff to prevent negligence and promote smart decisions
- Control access to data and applications via reliable, up-to-date measures, such as biometrics
- Implement protective data controls
- Control the use of monitors
- Encrypt data
- Secure mobile devices
- Manage connection risks by enabling a separate network for all IoT devices
- Conduct regular health checks
- Backup your data
- Monitor all market compliance instruments.
As it is clear that you cannot track all of this at once, I recommend that you allocate an in-house team, or more commonly, a trusted IT partner, to manage it in a reliable and customized way. My experience shows that you need to check a few key components when you choose one. The first one is that your potential outsourcer has intense compliance regulations experience. A good indication for this could be a couple of certifications like ISO 9001, or even better: ISO/IEC 27001, which defines handling security management systems. The second one is experience with digital healthcare projects.
Conclusion
The growth of digital healthcare is at an unprecedented level. We are witnessing a transition to an almost entirely digitized industry, which comes with both risks and opportunities. While embarking on this journey, your organization needs to consider all the data protection and security concerns that patients, system operators, and state and international regulations have. Being consistent, up to date, and mindful about it is what makes you compliant. So you should consider picking the best practices and solutions to make sure you succeed!